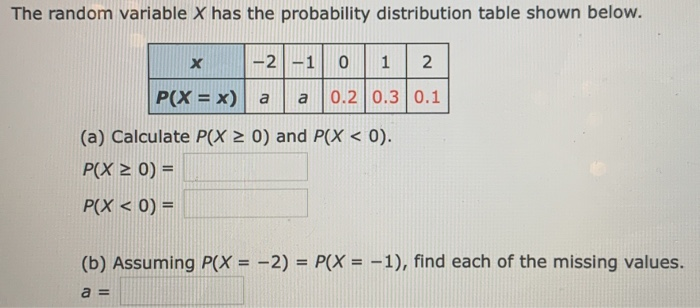
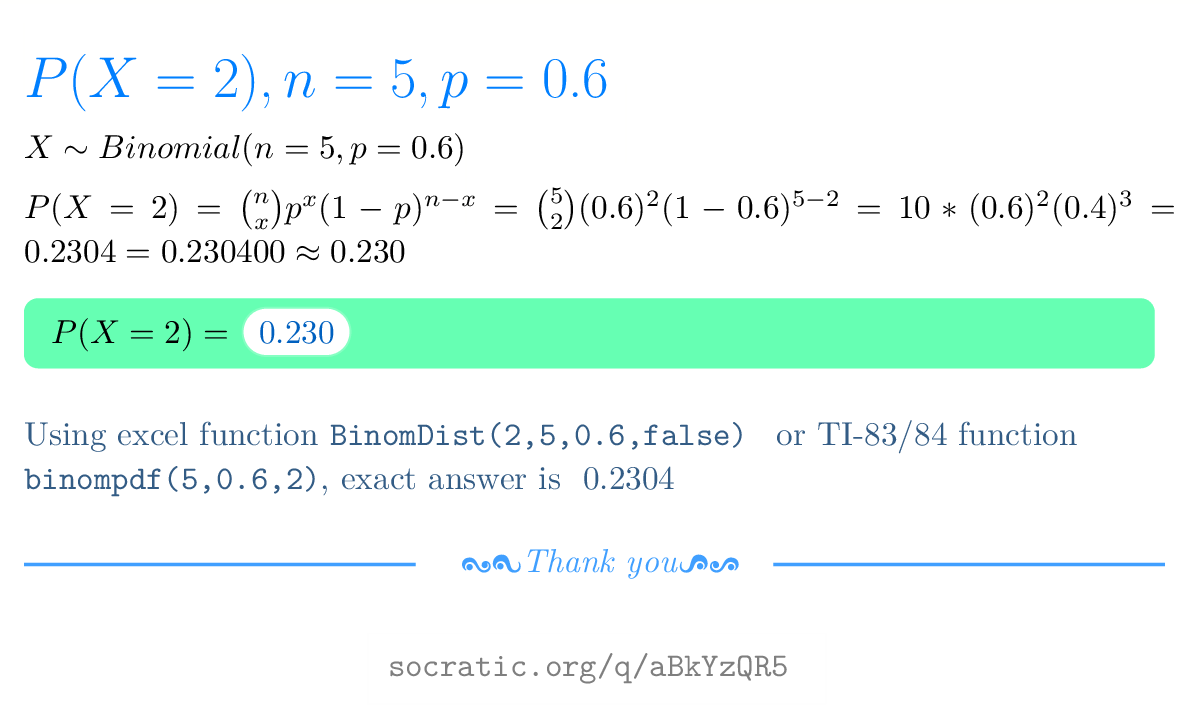
SOLVED: Consider the following cumulative probability distribution P(X < x) 0.17 0.30 0 . 48 0 . 75 0 . 88 a. Calculate AX < 4). (Round your answer to 2 decimal

If the probability density function of a random variable is given by, f(x) = { k(1 - x^2),& 0 < x < 1 0, & elsewhere . find k and the distribution function of the random variable.

SOLVED: Suppose X is a normally distributed random variable with p = 11 and 02 16 a ) Calculate P(X 8) (b) Calculate P(X 12) . Calculate P(11 < X 13). (d)
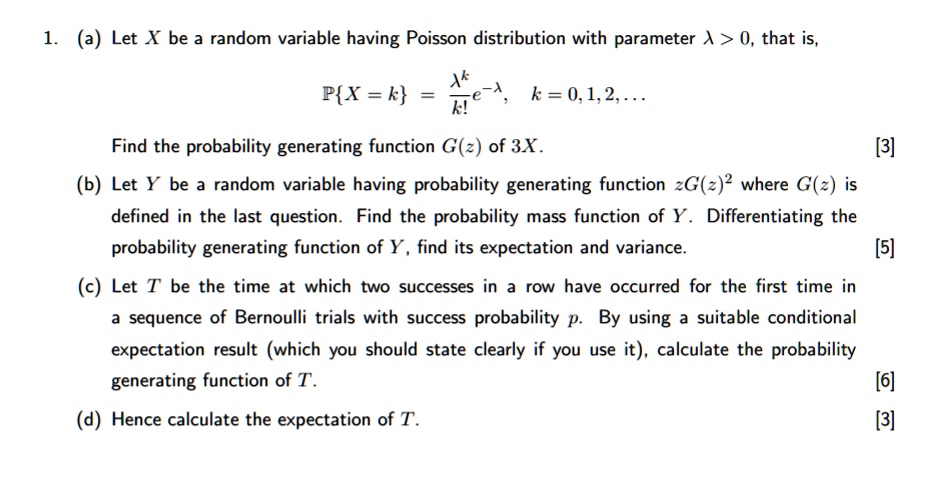
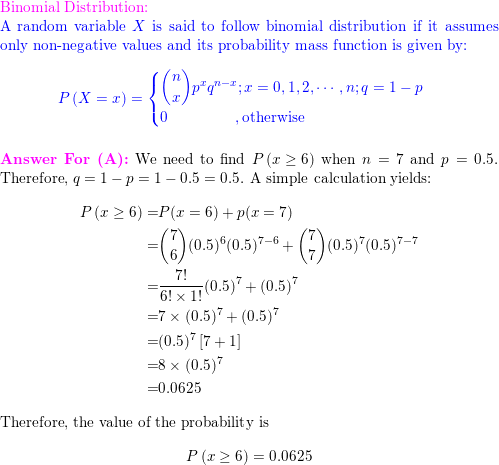
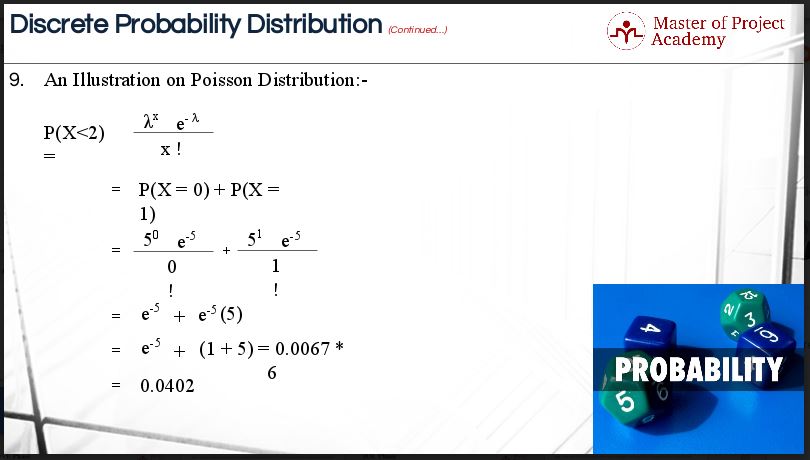
SOLVED: (a) Let X be a random variable having Poisson distribution with parameter > 0, that is, Ak e-4 k =0,1,2, k! PX = k Find the probability generating function G(2) of

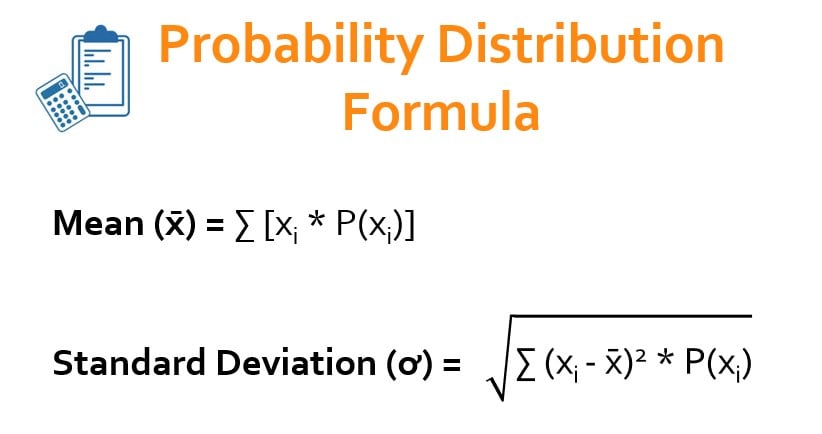
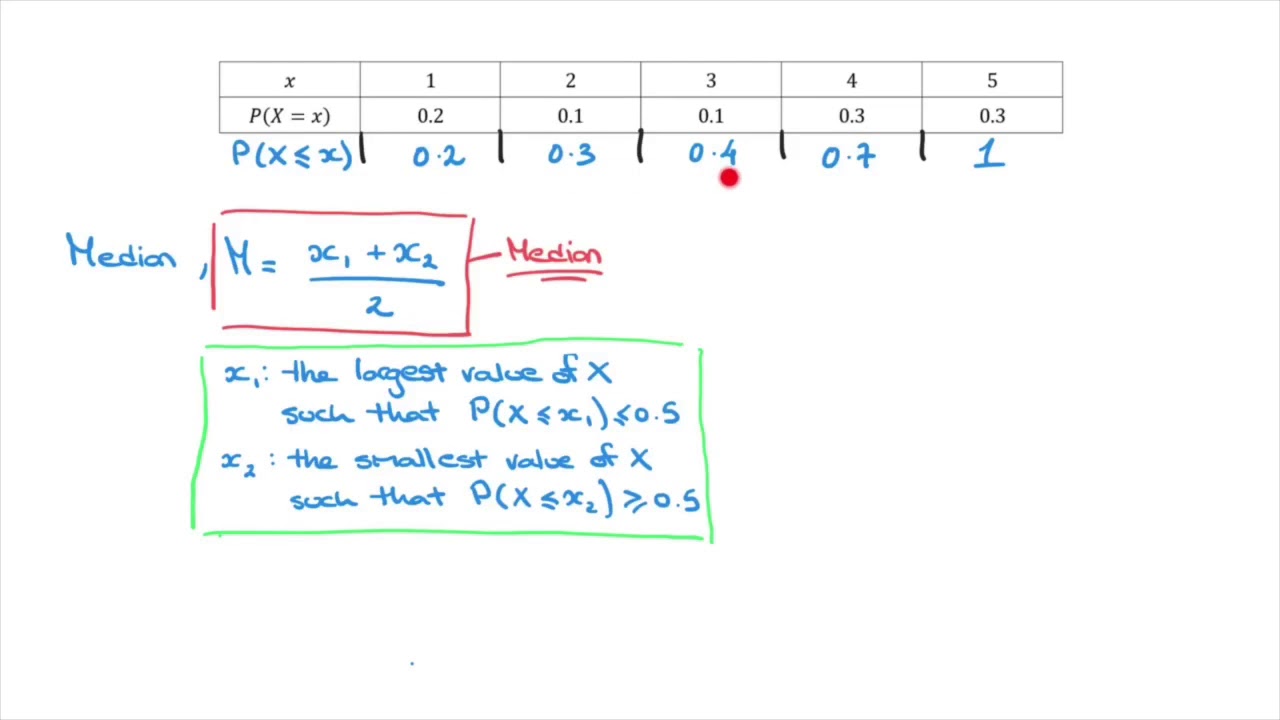
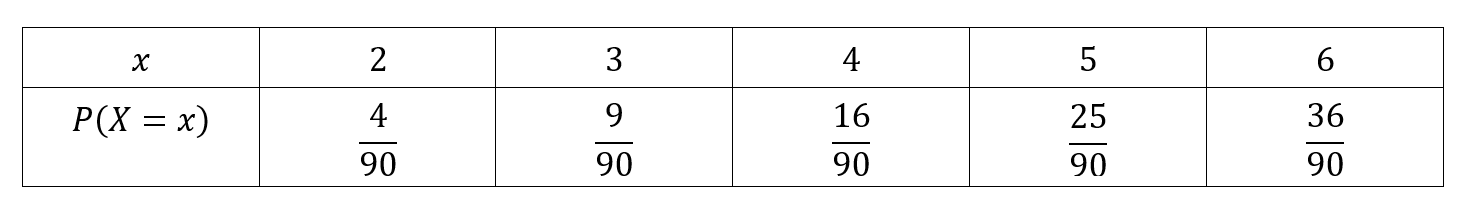
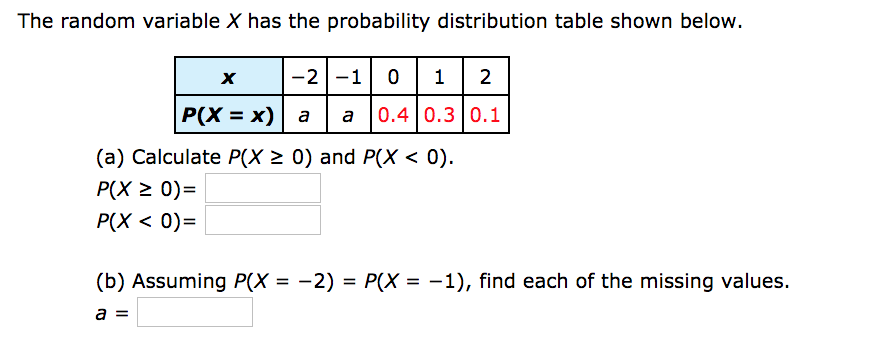
Calculate the mean for the probability distribution. Find k and P(X is greater or equal to 2) - YouTube
![SOLVED: [15 marks] The probability density function for a random variable X is given a8 52(1 f(r) = 1) , <T <1, otherwise (a) Calculate P(X < 1/3) (b)What is the probability SOLVED: [15 marks] The probability density function for a random variable X is given a8 52(1 f(r) = 1) , <T <1, otherwise (a) Calculate P(X < 1/3) (b)What is the probability](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/6940252104224b2c8fe336561dc1aa8c.jpg)